Knowledge Related to the Kjeldahl Nitrogen Analyzer
The Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer is a laboratory instrument used to determine the protein content in a sample. Its principle is based on measuring the amount of ammonia produced during the digestion process of the sample, which is then used to calculate the protein content. This method is one of the classic protein quantification techniques, with advantages such as high accuracy, good precision, and a wide range of applications.
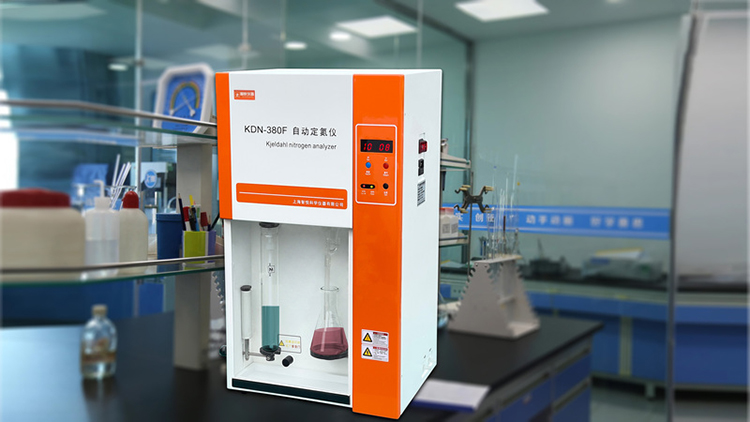

The principle of the Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer is based on the decomposition of proteins in the sample into ammonia gas under the action of a catalyst. The ammonia gas is distilled with distilled water, and then titrated with a reagent to calculate the protein content. Compared to other protein quantification methods, such as the BCA method or Lowry method, the Kjeldahl method offers better accuracy and precision.
The use of the Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer typically involves the following steps: First, sample preparation, which involves grinding the sample into a powder and mixing it thoroughly; second, digestion, where the sample is mixed with a catalyst and heated in a digestion furnace to decompose the proteins; third, distillation, where the digested mixture is transferred to a distillation apparatus to release the ammonia gas; and finally, titration, where the distilled ammonia gas is introduced into a receiving flask, and a titrant is added to determine the protein content.
When using the Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer, attention should be paid to the following points: First, sample preparation, which requires grinding the sample into a powder and ensuring uniform mixing to increase the surface area and homogeneity; second, the selection and storage of reagents, where appropriate reagents should be chosen and stored properly; and finally, safety precautions during operation, such as proper use of the digestion furnace and caution regarding the toxicity of catalysts and ammonia gas.
The Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer has many advantages, such as high accuracy, good precision, and a broad range of applications. However, it also has some drawbacks, such as a relatively complex operation process, which requires significant human effort and time. In addition, the method may have some limitations, such as potential errors when analyzing certain special samples.
Overall, the Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer, as a classic protein quantification method, has a wide range of applications in laboratories. It not only offers high accuracy and precision but is also suitable for a variety of different sample types. With ongoing advancements in technology, the operational processes and design of the Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer may be further optimized in the future, improving its applicability and efficiency.
More News