Determination of Protein Content in Oats Using Kjeldahl Nitrogen Determination
1. Introduction
Oats (scientific name: Avena sativa L.) are an annual herbaceous plant in the grass family, Poaceae, and the genus Avena. Oats are rich in protein content, which is 1.6 to 2.3 times higher than that of rice and wheat flour, making it the highest among the cereal grains. The protein in oats is of high nutritional value, containing 18 amino acids, 8 of which are essential for the human body. Therefore, consuming oat-based foods can help alleviate "lysine deficiency" caused by the dietary structure in China. Thus, testing the protein content in oats allows us to better understand their nutritional value.

2. Instruments and Reagents
2.1 Instruments
KDN-390F Automatic Kjeldahl Nitrogen Determinator
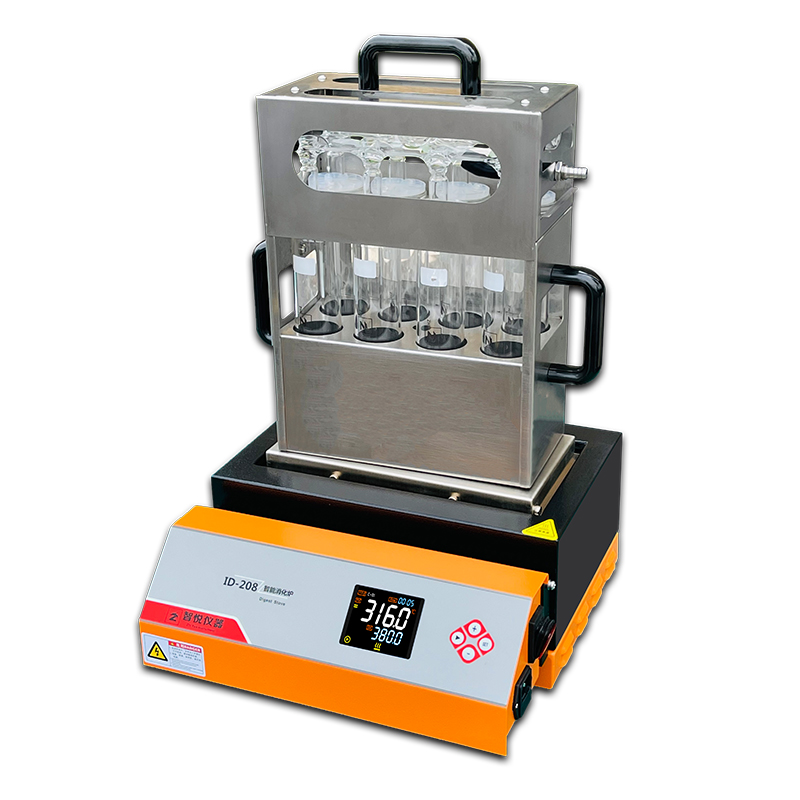
ID-208 Intelligent Digestion Furnace
Analytical Balance
2.2 Reagents
Concentrated sulfuric acid (analytical grade)
40% Sodium hydroxide
2% Boric acid solution
Bromocresol green-methyl red mixed indicator
Catalyst (K₂SO₄:CuSO₄ = 15:1, ground and mixed thoroughly for use)
0.0501 mol/L Sulfuric acid standard titrant
3. Experimental Method
3.1 Sampling
Accurately weigh approximately 0.3 g of the homogenized sample (to 0.0001 g), using weighing paper to tare the balance. Transfer the sample into the digestion tube without loss, avoiding contact with the tube walls. Add approximately 7 g of catalyst and carefully add 10 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid along the inner wall of the digestion tube using a pipette.
3.2 Digestion
Perform the digestion using the ID-208 intelligent digestion furnace. Carefully place the digestion tube on the furnace's digestion rack, cover it with the exhaust hood, connect the exhaust pump, open the water valve, and set the digestion parameters as shown in Table 1:
| Stage | Temperature (°C) | Holding Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200 | 5 |
| 2 | 250 | 5 |
| 3 | 300 | 5 |
| 4 | 350 | 10 |
| 5 | 400 | 5 |
| 6 | 420 | 60 |
3.3 Testing
After digestion, place the digestion tube onto the Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer. Set the analyzer parameters as follows:
Boric Acid: 4s
Dilution Water: 2s
Preheat: 10s
Alkali Solution: 10s
Distillation Time: 480s
Protein Coefficient: 6.25
Titrant Concentration: 0.0501 mol/L
4. Results and Discussion
4.1 Experimental Results
| Sample | Sample Weight (g) | Nitrogen Content (%) | Protein Content (%) | Average Value (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oats | 0.3004 | 2.4942 | 15.589 | 15.582 | 0.2 |
| 0.3112 | 2.4979 | 15.612 | |||
| 0.2998 | 2.4874 | 15.546 |
4.2 Conclusion
The test results show that the protein content in this oat sample is 15.582%, with an RSD value of less than 0.5%, indicating good repeatability. Furthermore, the absolute difference between the two independent test results obtained under the same conditions did not exceed 10% of the arithmetic mean.
References
[1] GB 5009.5-2016 National Food Safety Standard: Determination of Protein Content in Food[S].
More News